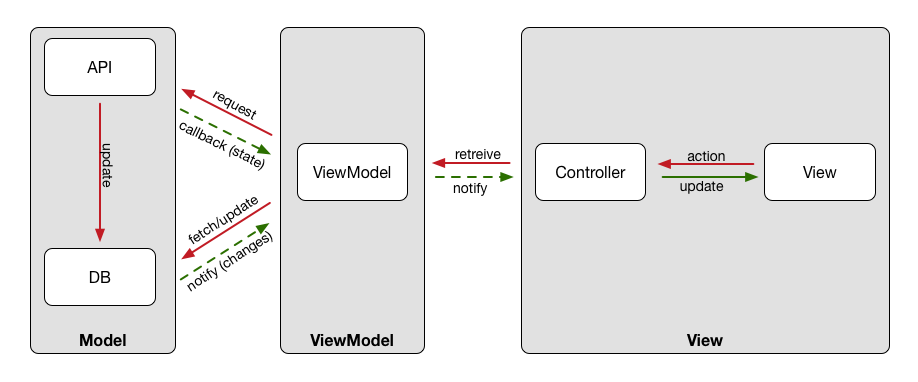
Riva Notes (just draft)
try try? try! 的使用時機
try
當開發者需要很完整的錯誤訊息,或是依據每個所拋出的錯誤的差異而有不同的事情要做時。
try?
當開發者必須做 Error Handling 時,又不太需要知道錯誤的種類,只需要知道有錯誤發生,並依照開發的需求適當的處理錯誤發生時要做的事情。
try!
當開發者非常、非常、非常確定絕對不會有錯誤產生,但又必須要做 Error Handling 時使用。
do try catch
※
do try catch是Error Handling最完整的寫法。
在使用do try catch時,我們必須將呼叫可能會拋出錯誤的方法及之後要做的事情包在 do{} 裡面,並在呼叫該方法前擺上 try 關鍵字,其後將錯誤出現時要做的事情放在 catch{}裡。
try!
會使用 try! 通常都是開發人員非常非常確定不會有錯誤產生的時候。
try?
在現實世界,問號通常都代表著不確定的因素。
由於 try? 不擁有 catch 功能,所以當方法拋出錯誤訊息時,開發者僅能得知有錯誤發生,卻不會得知錯誤訊息的種類。
「_(底線)」
用「_」(底線) 消除的忽略回傳值警告
用「 _=」 底線消除的忽略回傳值警告
無認何變數,取代為_(底線)
1
2
// 無認何變數,取代為_(底線)。
_ = semaphore.wait(timeout: DispatchTime.distantFuture)
將迴圈 i 取代為_(底線)
如果單純只是想要跑迴圈,並無任何變數可以將i取代為_(底線)
1
2
3
4
//如果單純只是想要跑迴圈,並無任何變數可以將i取代為_(底線)
for _ in 1 ... 3 {
print("Hi")
}
可變参数的函数 “…”
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
//可變参数的函数
func sum(input: Int...) -> Int {
//...
}
func sum(input: Int...) -> Int {
return input.reduce(0, combine: +)
}
print(sum(1,2,3,4,5))
// 输出:15
function 注意事項
call function時,參數後要指定參數名稱,不可以省略,如果要省略要加上底線
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
//call function時,參數後要指定參數名稱,不可以省略
func plus(a :Int, b:Int){
print(a+b)
}
plus(a:1, b:3)
//如果要省略要加上底線
func plus(_ a :Int,_ b:Int){
print(a+b)
}
plus(1, 3)
外部參數名稱(External parameter Name)
事實上a前面的底線是External parameter Name的意思。
External parameter Name用於外部呼叫Function時的參數識別名,若不寫則與內部名稱相同。
而底線代表不在意參數識別名稱,即為可忽略的意思。
1
2
3
4
func plus(AAA a :Int,BBB b:Int){
print(a+b)
}
plus(AAA:1, BBB:3)
guard的用途
guard比if能更好的實行Defensive Programming,
因為在guard中的可選綁定可以在接下來code中使用。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
var text:String? = "abc"
if let apple = text{
print(apple)
}
// 在這邊用會失敗
// print(apple)
var text:String? = "abc"
guard let apple = text else{
print(apple)
}
// 照用
print(apple)
Error
Swift丟出的異常是一種enum,實作時繼承Error。
有幾種方法:
- 最基本的
do try catch - 向上拋擲
function填throw try?: 如果出現錯誤則回傳nil(不用再寫do catch),可搭配optinal bindingtry!: 一定成功。(若沒成功會crash)
Need to know
weak & unowned
[weak self, unowned inputCell]
1
[weak self, unowned inputCell]
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
// A class
var resignationHandler: (() -> Void)?
func textFieldDidEndEditing(_ textField: UITextField) {
resignationHandler?()
}
// B class
inputCell.resignationHandler = {
[weak self, unowned inputCell] in
if let text = inputCell.textField.text {
self?.emojis = (text.map { String($0) } + self!.emojis).uniquified
}
self?.addingEmoji = false // 將新增狀態設為 false
self?.emojiCollectionView.reloadData() // 更新 emoji 資料
}
Others
什麼狀況會造成reference迴圈?
A: 當a,b互相delegate對方時,就算a release掉 還是會存在在記憶體中,必須兩人都 release 掉才行
1
2
a.delegate = b
b.delegate = a
用 try? 解析 JSON (draft)
1
2
3
4
5
6
//try?才是真正我一開始想要的處理過程:當有 error 要抛出的時候,會進到 else 程式碼區塊中
guard let jsonDict = try? NSJSONSerialization.JSONObjectWithData(data, options: .AllowFragments) as? [String : AnyObject],
// Notice the extra question mark here!
todoListDict = jsonDict?["todos"] as? [[String : AnyObject]] else {
throw Error.InvalidJSON
}
nothing (test)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
[Swift4][Sqlite3]
select
sqlite3_prepare_v2 == SQLITE_OK
sqlite3_bind_text == SQLITE_OK
sqlite3_step == SQLITE_ROW
sqlite3_finalize(statement)
insert
sqlite3_prepare_v2 == SQLITE_OK
sqlite3_bind_text == SQLITE_OK
sqlite3_step == SQLITE_DONE
sqlite3_finalize(statement)
使用sqlite3_exec方法可以執行一段sql語句
sqlite3_exec == SQLITE_OK
sqlite3_finalize(statement)
[Swift][PlaygroundPage][TableView]
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
class WWDCMasterViewController: UITableViewController {
var reasons = ["WWDC is great", "the people are awesome", "I love lab works", "key of success"]
override func viewDidLoad() {
title = "Reason I should attend WWDC18"
view.backgroundColor = .lightGray
}
override func tableView(_ tableView: UITableView, numberOfRowsInSection section: Int) -> Int {
return self.reasons.count
}
override func tableView(_ tableView: UITableView, cellForRowAt indexPath: IndexPath) -> UITableViewCell {
var cell: UITableViewCell! = tableView.dequeueReusableCell(withIdentifier: "Cell")
if cell == nil {
cell = UITableViewCell(style: .subtitle , reuseIdentifier: "Cell")
cell.accessoryType = .disclosureIndicator
}
let reason = reasons[indexPath.row]
cell.detailTextLabel?.text = "I want to attend because\(reason)"
cell.textLabel?.text = "Reason #\(indexPath.row + 1)"
return cell
}
}
let master = WWDCMasterViewController()
let nav = UINavigationController(rootViewController: master)
PlaygroundPage.current.liveView = nav
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
let nextButton: UIButton = {
let button = UIButton()
button.backgroundColor = UIColor.white
button.setTitleColor(.red, for: .normal)
button.setTitle("Hi 您好", for: .normal)
button.translatesAutoresizingMaskIntoConstraints = false
button.addTarget(self, action: #selector(nextButtonClick), for: .touchUpInside)
return button
}()
view.addSubview(nextButton)
setupLayoutConstrains()
@objc func nextButtonClick(sender: UIButton) {
let button = sender
let text = button.titleLabel?.text
let postListController = PostListController()
postListController.title = text
navigationController?.pushViewController(postListController, animated: true)
}
func setupLayoutConstrains() {
nextButton.leadingAnchor.constraint(equalTo: view.leadingAnchor, constant: 20).isActive = true
nextButton.trailingAnchor.constraint(equalTo: view.trailingAnchor, constant: -20).isActive = true
nextButton.heightAnchor.constraint(equalToConstant: 50).isActive = true
nextButton.centerYAnchor.constraint(equalTo: view.centerYAnchor).isActive = true
}
//==============
//Model
class Article {
var title: String
var body: String
var date: NSDate
var thumbnail: NSURL
var saved: Bool
}
//Controller
class ArticleViewController: UIViewController {
var bodyTextView: UITextView
var titleLabel: UILabel
var dateLabel: UILabel
var article: Article {
didSet {
titleLabel.text = article.title
bodyTextView.text = article.body
let dateFormatter = NSDateFormatter()
dateFormatter.dateStyle = NSDateFormatterStyle.ShortStyle
dateLabel.text = dateFormatter.stringFromDate(article.date)
}
}
}
- TODO see: delegate、protocol、tagart-action、closure
- CGRect 就是iOS 中,一個UIView 的「origin (開始位置)」與「size (大小)」的表示方式。
Stanford CS193p - Developing Apps for iOS (斯坦福(Stanford) CS193p)
[Swift] Questions that may be asked in the interview. by R
Swift is a lot like C# by R